前言
通过联合NBI放大内视镜(M-NBI)的开发运用,我们可以清晰地看到胃粘膜上皮下的微血管的形态结构(V)和表面的微观结构(S)。以V和S作为指标,八尾等学者建立了放大内视镜的新胃癌诊断体系【VS(vessel plus surface)classification system:VSCS】,使M-NBI的胃癌定性诊断能力比普通内视镜(conventional white light image:C-WLI)有了飞跃性的提高。
M-NBI的有效性研究报告虽然很多,其中【以所有肉眼观察的常规检查为对象,用VSCS的M-NBI进行了一项前瞻性多中心可行性研究】的结果,成为了促使M-NBI导入常规检查的有力证据。在这项前瞻性研究里,虽然对于平坦型褪色的病变,M-NBI诊断能力有其局限性,但是对于泛红以及同一颜色的病变,M-NBI都有非常高的诊断能力。也就是说,用VSCS的M-NBI对于胃病变中的癌变鉴别非常有效,可以认为是一个光活检。此外,除了系统的诊断系统利用VSCS,已陆续报道是接近病理组织图像M-NBI的新知识。
在本文中,我们也融合这些新知识,来描述在胃的病变(胃炎,腺瘤,胃癌的鉴别诊断)中如何使用VSCS的M-NBI诊断。
M-NBI观察方法
在笔者的研究设施里,由于侧重于微血管的形态结构图像(V)的分析评估,所以将M-NBI观察条件设定为构建增强B8和NBI彩色模式。尽管是在常规检查里导入的M-NBI,但即使在常规检查时black soft hood也是必不可少的。Black soft hood的深度是最大倍率观察的焦距,即2mm。在最大倍率观察时尽可能配合使用浸水观察方法。
原则上,我们对微血管形态结构图像(V),表面的微观结构(S),以及边界线(分界线:DL)分别独立地进行判定。根据V,S,以及DL的判定结果的组合,其irregular MV(microvascular)pattern with a DL的情况,或者irregular MS(microsurface)pattern with a DL的情况,这两种情况中的任意一种或者是两种情况都存在时,诊断为癌病变。两种情况都没有的话,诊断为非癌病变的腺瘤。
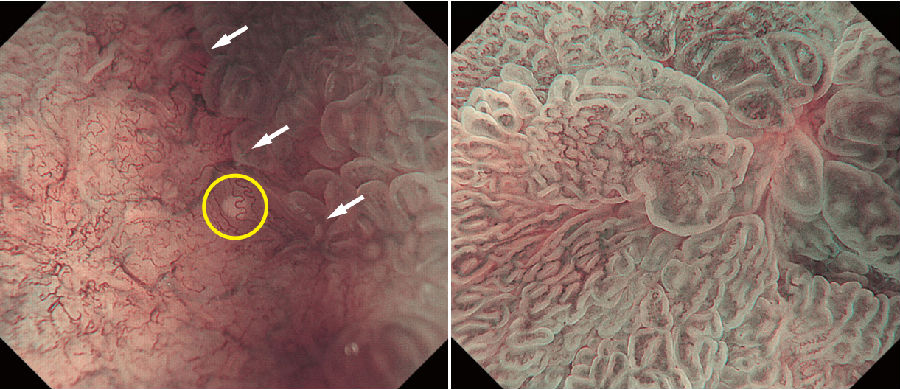
![]()
a图:M-NBI早期胃癌及其分界部的最大倍率观察画像。0-IIc,高分化型腺癌。M-NBI诊断:癌病变,VSCS。 病变的内侧和外侧急剧的变化,可以观察到清晰的DL(白色箭头所示)。对于V,各个血管的闭合性或者是开放性的循环状,观察不到同一个形态。形状不一致,分布非对称性,排列不规则,判定为imvp。对于S,基本观察不到MCE,判定为absent MS pattern。另外,DL附近可以观察到WGA(黄色圆圈部分所示)。
b图:M-NBI的非癌病变的最大放大倍率观察画像。伴随肠上皮化生的慢性萎缩性胃炎。M-NBI诊断:非癌病变。VS渐渐发生了变化,判定DL为absent。观察不到VS的形状、分布、排列的不规则性,判定为regular。
基于VSCS的M-NBI诊断标准
1.DL的判定
我们把DL的判定结果用present/absent(存在/不存在)来标记。如果观察到病变内测与外侧V或S有急剧的变化,能清晰地认识出分界线时,我们将其标记DL present。如果V和S是逐渐改变,则标记为DL absent。另外,只有在DL absent时,才有极高的概率来排除癌病变的可能性。
2.V的判定
我们把V的判定结果用regular /irregular/absent(规则/不规则/缺失)来标记。通过对微血管的形态以及它们之间相互形态(形状,分布,序列)的判定,其综合判定的结果是irregular时,就可以判定为irregular MV pattern。
3.S的判定
我们把S的判定结果用regular /irregular/absent(规则/不规则/缺失)来标记。通过对微血管的表面的微观结构的形态以及它们之间相互形态(形状,分布,序列)的判定,其综合判定的结果是irregular时,就可以判定为irregular MV pattern。另外,腺窝边缘上皮(marginal crypt epithelium:MCE)、腺孔(crypt opening:CO),窝间部(intervening part:IP)、LBC(light blue crest)、白色不透明物质(white opaque substance:WOS)等,它们是用于S判定的观察对象,其任意一个清晰的观察结果都可以作为S判定的指标。
M-NBI对病理组织像的新发现
1. 白色球状外观(white globe appearance:WGA)
在最大放大倍率M-NBI放大观察早期胃癌时,有时会观察到肿瘤上皮的血管(黄色圆圈部分所示)下方有小于1mm的的白色球体。我们把这个白色球体命名为WGA。
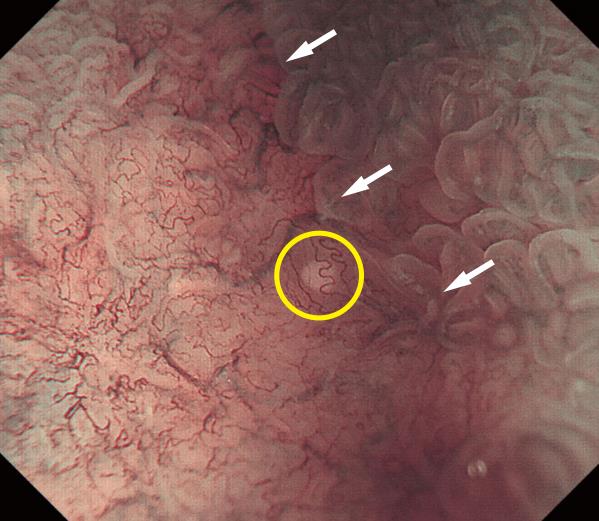
通过细致地组织学调查所示,WGA是那些扩张的腺管内的上皮组织的坏死碎片的沉积物IND(intraglandular necrotic debris)。
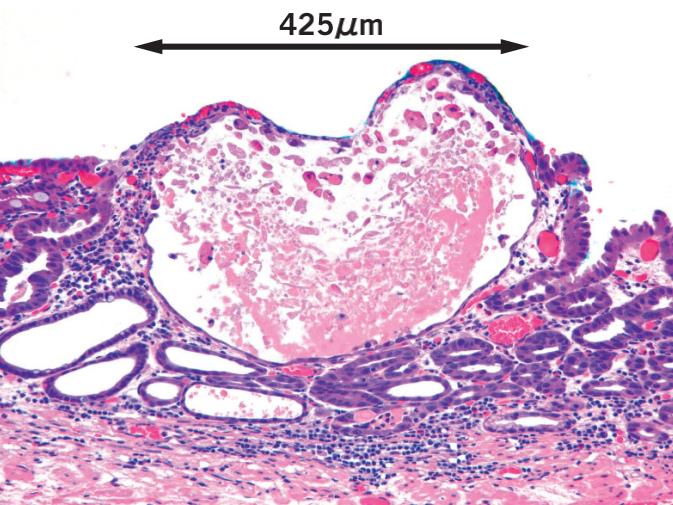
已有研究表明,这些IND就是诱发癌症的特殊病理标记。在对WGA的临床意义的研究时发现,目前在早期胃癌的约20%存在WGA,特别是在1cm以下时约40%存在WGA。
在另一方面,WGA根本没有在胃内腺瘤被观察到的,在胃炎只有2.5%存在WGA。由于WGA具有非常高的特异性,放大内镜检查结果观察到WGA的话,那么可以将那些非癌性的如腺瘤或胃炎等疾病与癌病变相当准确地鉴别出来。
2. 上皮环内血管(vessels within epithelial circle:VEC)pattern
上皮环内血管是,在放大内视镜观察下,为环形MCE包绕形成的环形IP上皮范围内血管。我们可以取得含有乳头状腺癌的组织学乳头状结构的这一特异性的观察结果。具有VEC分化型癌症与不具有VEC分化型癌症相比,未分化混在和粘膜下层浸润的程度,可以认为是恶性程度高的分化型癌变的一个指标。
3.VS discordance
VS discordance是指M-NBI观察下,围绕MCE的IP上皮下通常具有稳定分布的微血管发生了崩溃,MCE和微血管的分布和走行出现了偏离的情况。这个特征常见于异型度高的癌病变和浸润癌病变。
4.dense-type CO
在环状闭合型血管中心看上去是狭缝状的CO,以最大倍率的M-NBI观察时,视野里出现20个以上的情况时,定义为dense-type CO阳性,我们把它作为腺肿瘤诊断的指标。因为腺肿瘤,它是由在垂直方向上有序排列的MCE形成的CO,很容易被看成为狭缝状。
总结
VS分类中的NBI放大诊断标准
微血管形态结构图像(V)
表面的微观结构图像(S)
边界线(DL)
以上三种表现分别独立进行判定。
1.V的判断
我们把V的判断结果用regular/irregular/absent(规则/不规则/缺失)来作为标记。通过对微血管的形态以及它们之间的形态改变,分布,排列来判断。
2.S的判断
我们把S的判断结果用regular/irregular/absent(规则/不规则/缺失)来作为标记。通过对微血管的表面微结构形态以及它们之间的形态改变、分布、排列来判断。
参考文献
1) Muto M, Katada C, Sano Y, et al. Narrow band imaging:a new diagnostic approach to visualize angiogenesis in the su?perficial neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:16-20,
2005
2) Yao K, Takaki Y, Matsui T, et al. Clinical application of mag?nification endoscopy and narrow-band imaging in the upper gastrointestinal tract:new imaging techniques for detecting and characterizing gastrointestinal neoplasia. Gastrointest En?dosc Clin N Am 18:415-433, 2008
3) Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Ragunath K. Magnifying endos?copy for di- agnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. En?doscopy 41:462-467, 2009
4) Kato M, Kaise M, Yonezawa J, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging achieves superior accuracy in the differential diagnosis of superficial gastric lesions identified with white-light endoscopy:a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 72:523-529, 2010
5) Ezoe Y, Muto M, Uedo N, et al. Magnifying narrow-band im?aging is more accurate than conventional white-light imaging in diagnosis of gastric mucosal cancer. Gastroenterology 141:2017-2025, 2011
6) Okada K, Fujisaki J, Kasuga A, et al. Diagnosis of undifferen?tiated type early gastric cancers by magnification endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:
1262-1269, 2011
7) Miwa K, Doyama H, Ito R, et al. Can magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging be useful for low grade adenomas in preoperative biopsy specimens? Gastric Cancer 15:170-
178, 2012
8) Yao K, Doyama H, Gotoda T, et al. Diagnostic performance and limitations of magnifying narrow-band imaging in screen?ing endoscopy of early gastric cancer:a prospective multi?center feasibility study. Gastric Cancer 17:669-679, 2014
9) Fujiwara S, Yao K, Nagahama T, et al. Can we accurately diag?nose minute gastric cancers(≦5mm) ? Chromoendoscopy(CE)vs magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging(M-NBI). Gastric Cancer 18:590-596, 2015
10) Yamada S, Doyama H, Yao K, et al. An efficient diagnostic strategy for small, depressed early gastric cancer with magnify?ing narrow-band imaging:a post-hoc analysis of a prospective randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 79:55-63, 2014
11) Uedo N, Ishihara R, Iishi H, et al. A new method of diagnos?ing gastric intestinal metaplasia:narrow-band imaging withmagnifying endoscopy. Endoscopy 38:819-824, 2006
12) Yao K, Iwashita A, Tanabe H, et al. White opaque substance within superficial elevated gastric neoplasia as visualized by magnification endoscopy with narrow-band imaging:a new
optical sign for differentiating between adenoma and carcino?ma. Gastrointest Endosc 68:574-580, 2008
13) Yao K, Iwashita A, Nambu M, et al. Nature of white opaque substance in gastric epithelial neoplasia as visualized by magni?fying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. Dig Endosc 24:419-425, 2012
14) Doyama H, Yoshida N, Tsuyama S, et al. The “white globe ap?pearance”(WGA):a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with nar?row-band imaging(M-NBI). Endosc Int Open 3:E120-124, 2015
15) Yoshida N, Doyama H, Nakanishi H, et al. White globe ap?pearance is a novel specific endoscopic marker for gastric can?cer:A prospective study. Dig Endosc e-Pub ahead, 2015 Jul 31
16) Watanabe Y, Shimizu M, Itoh T, et al. Intraglandular necrotic debris in gastric biopsy and surgical specimens. Ann Diagn Pathol 5:141-147, 2001
17)八尾建史,松井敏幸(監),岩下明德.胃拡大内視鏡.日本メ ディカルセンター,2009
Stomach and Intestine (Tokyo) Vol. 51 No. 5 2016 603
18) Kanemitsu T, Yao K, Nagahama T, et al. The vessels within epithelial circle(VEC)pattern as visualized by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging(ME-NBI)is a useful marker for the diagnosis of papillary adenocarcinoma:a case-controlled study. Gastric Cancer 17:469-477, 2014
19) Kanesaka T, Sekikawa A, Tsumura T, et al. Dense-type crypt opening seen on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging is a feature of gastric adenoma. Dig Endosc 26:57-62,
2014
20)長浜孝,小島俊樹,八尾建史,他.胃扁平隆起型腺腫と0-IIa 型病変の鑑別診断における非熟練者に対する狭帯域光観察 併用拡大内視鏡の有用性と問題点.胃と腸 49:1815-1826, 2014
21)八尾建史.動画で学ぶ胃拡大内視鏡テクニック.日本メディカルセンター,2012
来源:医脉通